Getting Started with DBEdit for Database Editing
To get started with DBEdit, create a workbook that includes your first connected worksheet.
Next, insert worksheets that connect to other objects.
You can save your workbook and reopen it later. By default, workbooks have the .dbsx extension.
The primary purpose of DBEdit is to edit database data.
In the toolbar, you'll find two green buttons for saving changes and reloading data (or use Ctrl-F5 and Alt-F5, respectively):
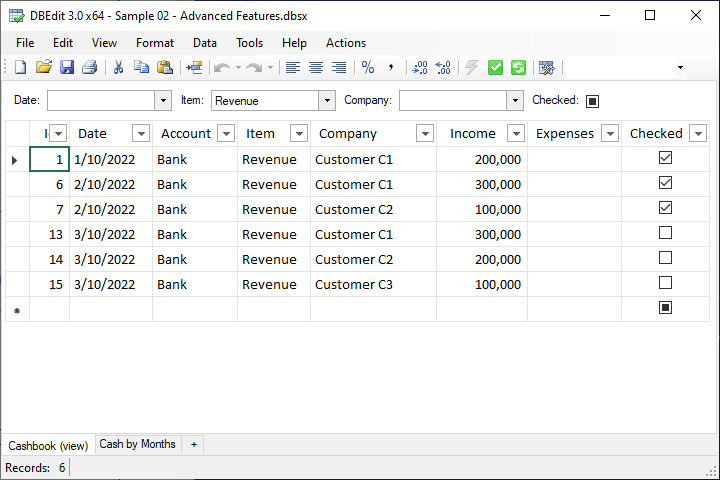
Keep in mind that saving a workbook and saving data changes are distinct actions.
For example, you can modify data, save and close the workbook, then reopen it later to save the changes to the database.
DBEdit includes many essential features found in spreadsheet applications like Microsoft Excel.
Check out the application menu to explore the available actions.
DBEdit offers even more features when configured.
For instance, it can utilize stored procedures in the context menu to retrieve details:
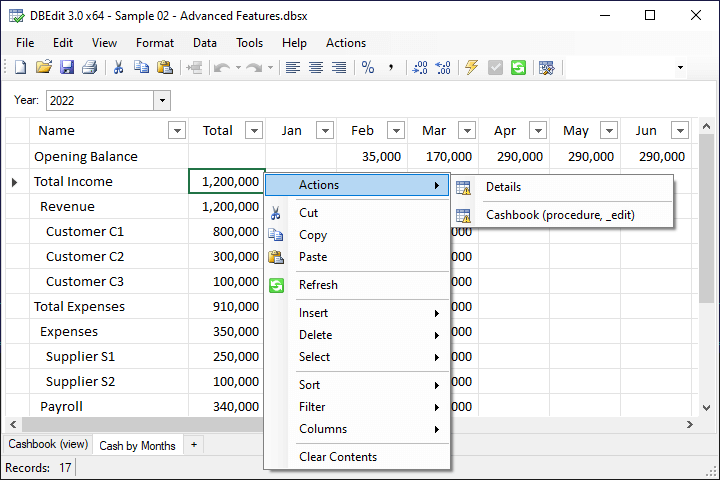
You'll notice that the save button is disabled while the yellow arrow button is enabled.
The yellow button indicates that the table has a change handler, allowing DBEdit to save data immediately after any cell change.
This feature requires server-side configuration.
Database developers can easily create editable reports like this.